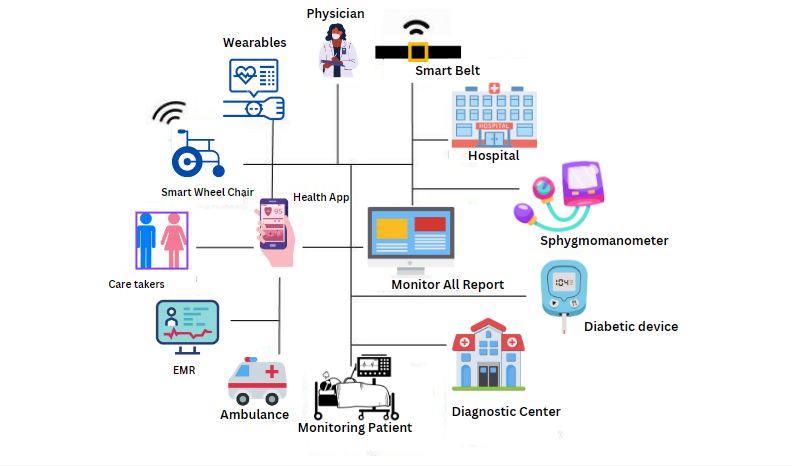
Cybersecurity and Privacy Issues in the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
Keywords:
Cybersecurity, Privacy, Internet of Medical Things, IoMT, Data breachesAbstract
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry by providing real-time health information, remote monitoring, and improved treatment options. With this increased connectivity comes an increased risk of cybersecurity and privacy issues. This research study aimed to identify and analyze the key cybersecurity and privacy issues associated with the IoMT and provide recommendations for healthcare providers and device manufacturers to address these issues. Data breaches were identified as a significant cybersecurity risk associated with the IoMT. The IoMT collects and transmits sensitive medical data, such as patient health records and medical device data. This data is highly valuable to hackers and can be used for identity theft, insurance fraud, and other malicious activities. The study found that implementing strong authentication and access controls, using encryption to protect data in transit and at rest, regularly updating and patching devices, and training employees on cybersecurity best practices can help mitigate this risk. The research revealed vulnerable devices as a significant cybersecurity risk associated with the IoMT. Many medical devices are not designed with security in mind, which makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in these devices to gain access to sensitive data or to take control of the device. The study found that healthcare providers and device manufacturers must prioritize cybersecurity in the design, implementation, and maintenance of IoMT systems. This includes regularly updating and patching devices and implementing security protocols to protect against known vulnerabilities. The lack of encryption was identified as another significant cybersecurity risk associated with the IoMT. Data transmitted over the IoMT may not always be encrypted, leaving it vulnerable to interception by hackers. The study found that implementing encryption technologies such as secure sockets layer (SSL) and transport layer security (TLS) can help protect data in transit. Insider threats were identified as a significant cybersecurity risk associated with the IoMT. Healthcare employees and other authorized users may accidentally or intentionally leak sensitive data, either through negligence or malicious intent. The study found that implementing role-based access control, conducting regular security awareness training, and implementing auditing and monitoring tools can help mitigate this risk. IoMT must comply with various regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The study found that compliance with these regulations can be challenging, and non-compliance can result in fines and legal penalties. Healthcare providers and device manufacturers must prioritize regulatory compliance in the design, implementation, and maintenance of IoMT systems.